In-vitro Evaluation of Irrigants for the Removal of Smear Layers
In-vitro Evaluation of Irrigants for the Removal of Smear Layers
Dr. Nektarios Tsoromokos*
*Correspondence to: Dr. Nektarios Tsoromokos, Periodontal Practice Zwolle (PPZ) and PROCLIN Rotterdam, Periodontist and implantologist in private practice, Netherlands.
Copyright.
© 2024 Dr. Nektarios Tsoromokos. This is an open access article distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Received: 30 Sep 2024
Published: 18 Oct 2024
In-vitro Evaluation of Irrigants for the Removal of Smear Layers
Introduction
The smear layer formed during canal preparation can cause failure by blocking the dentinal tubule, preventing sealer penetration and hampering bonding. Improper obturation can lead to microleakage and bacteria in the smear layer. Various irrigating materials and solutions are being studied for removing the smear layer. An in-vitro SEM study will use a scanning electron microscope to analyze the effectiveness of different root canal irrigation solutions in removing the smear layer on extracted teeth. This will allow researchers to visually compare the degree of smear layer removal between different irrigants under high magnification.
Material and Method
All the teeth (N - 50) were decoronated and prepared with the help of # 10-15 K files, Followed by biomechanical preparation with the help of Blueflex files #20-25-30 with 6% taper. Each root canal was prepared to the size of 30 with a 06% taper on the apically. Simultaneously, irrigation was done with the help of Sodium Hypo chloride (NaOCl) 2ml of 5.25%, and final irrigation was done with the help of side vented 30 gauge needles which were 1-2 mm short of apex with different irrigation according to the group. The irrigants were NaOCl, Q mix, MTAD, EDTA, and Apple Vinegar, Followed by drying and examination of all the samples under SEM for smear layer deposition in the apical third of the canal region.
Grouping of Samples
On the basis of irrigants used in the study – (fig 3)
Sample preparation:
Collect extracted human teeth with intact root canals.
Prepare root canals using standardized instrumentation techniques.
Divide the samples into groups, each assigned to a different irrigant (e.g., sodium hypochlorite (NaOCl), ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA), MTAD, etc.).
Irrigation procedure:
Irrigate each root canal with the allocated irrigant solution using a standardized protocol.
Consider different irrigation techniques like passive ultrasonic irrigation or conventional syringe irrigation.
SEM analysis:
After irrigation, carefully split the teeth longitudinally to expose the root canal walls.
Dehydrate and mount the specimens on SEM stubs.
Coat the samples with a thin layer of gold using a sputter coater.
Examine the root canal surfaces under SEM at high magnification to assess the presence or absence of smear layer, noting the degree of dentinal tubule opening.
Data analysis:
Score the smear layer removal on each sample using a standardized scoring system (e.g., based on the extent of tubule opening, debris coverage).
Compare the mean smear layer scores across different irrigant groups using statistical analysis to identify which irrigant was most effective in removing the smear layer.
Standardized instrumentation:
Use consistent root canal preparation techniques to minimize variability in smear layer formation.
Blinding:
Randomly assign samples to different irrigant groups to minimize bias during analysis.
Sample size:
Include a sufficient number of samples per group to ensure statistically reliable results.
Qmix, EDTA, MTAD, Apple vinegar, NaOCl(Fig 4,5,6,7,8)
Fig 9
PAIR WISE COMPARSION
|
|
GROUP 2: EDTA |
GROUP 3: Q MIX |
GROUP 4: APPLE VINEGAR |
GROUP 5: MTAD |
|
GROUP 1: CONTROL |
0.002*, SIG |
0.001*, SIG |
0.393, NS |
0.001*, SIG |
|
GROUP 2: EDTA |
- |
0.132, NS |
0.001*, SIG |
0.436, NS |
|
GROUP 3: Q MIX |
- |
- |
0.001*,SIG |
0.631, NS |
|
GROUP 4: APPLE VINEGAR |
- |
- |
- |
0.001*, SIG |
|
GROUP 5: MTAD |
- |
- |
- |
- |
MANN WHITNEY U TEST
LEVEL OF SIGNIFICANCE SET AT P ≤ 0.05
SIG: SIGNIFICANT
NS: NON SIGNIFICANT
Figure 1
Armamentarium used in the procedure
1. Endomotor (TROUSENDO) 2 Syringe (NIPRO) 3.K file no # 10-15 (MANI) 4. Vernier calliper 5. 30 gauge side-vented needle (DENTSPLY ProRinse) 6. Micro motor and straight hand piece (API) 7. Paper points (DIADENT) 8. Blue flex rotary file (BLUE FELX) 9. Endo gauge(DENTSPLY) 10. Contra angle Airrotor (APPLEDENT) 11. Beaker (Borosil) 12. Chisel and mallet(API)
Figure – 2 Material used in the study
1. Sodium hypochloride 5% (DENTPRO) 2. Apple vinegar 5%(HEINZ) 3. EDTA(CANALARGE) 4. Q-mix 2in1(DENTSPLY) 5. MTAD(DENTSPLY)
Conclusion
This study evaluated the effectiveness of various irrigants in removing the smear layer from the apical third of root canals. The results indicated that Q mix demonstrated statistically significant smear layer removal compared to other irrigants, proving to be the most effective in ensuring a clean dentinal surface. In contrast, Apple Vinegar showed the least effectiveness in smear layer removal. These findings emphasize the importance of selecting appropriate irrigants to optimize root canal cleaning, prevent microleakage, and enhance the overall success of endodontic treatment.
Reference
1.Dai L, Khechen K, Khan S, Gillen B, Loushine BA, Wimmer CE,et al. The effect of QMix, an experimental antibacterial root canal irrigant, on removal of canal wall smear layer and debris. J Endod 2011;37:80?84.
2.Torabinejad M, Khademi AA, Babagoli J, Cho Y, Johnson WB, Bozhilov K, et al. new solution for the removal of the smear layer. J Endod 2003;29:170?175.
3.Giardino L, Ambu E, Savoldi E, Rimondini R, Cassanelli C, Debbia EA, et al. Comparative evaluation of antimicrobial efficacy of sodium hypochlorite, MTAD, and tetraclean against Enterococcus faecalis biofilm. J Endod 2007;33:852?855
4.Hülsmann M, Heckendorff M, Lennon A. Chelating agents in root canal treatment: mode of action and indications for their use. International endodontic journal. 2003 Dec;36(12):810-30.
5.Johal S, Baumgartner JC, Marshall G. Comparison of the antimicrobial efficacy of 1,3% NaOCl/BioPure MTAD to 5,25% NaOCl/15% EDTA for root canal irrigation. J Endod 2007;33:48-51.
6. Mohanty S, Ramesh S, Muralidharan NP. Antimicrobial efficacy of apple cider vinegar against Enterococcus faecalis and Candida albicans: An in vitro study. J Adv Pharm Edu Res 2017;7(2):137-141.
7.Singla MG, Relhan N, Aggarwal H. Comparative evaluation of oxytetracycline versus QMix, MTAD, and ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid as smear layer removal agents: An in vitro study. Endodontology 2018;30:2-8.
8.Candeiro GT, Matos IB, Costa CF, Fonteles CS, Vale MS. A comparative scanning electron microscopy evaluation of smear layer removal with apple vinegar and sodium hypochlorite associated with EDTA. Journal of Applied Oral Science. 2011 Dec;19(6):639-43
9.Khademi A, Yazdizadeh M, Feizianfard M. Determination of the minimum instrumentation size for penetration of irrigants to the apical third of root canal systems. Journal of endodontics. 2006 May 1;32(5):417-20..
10.Harrison JW. Irrigation of the root canal system. Dental Clinics of North America. 1984 Oct 1;28(4):797-808.
11. Akcay I, Sen BH. The effect of surfactant addition to EDTA on microhardness of root dentin. Journal of Endodontics. 2012 May 1;38(5):704-7.
12. Topbas C, Adiguzel O. Endodontic irrigation solutions: A Review. International Dental Research. 2017 Dec 31;7(3):54-61.
13. Aniketh TN, Idris M, Geeta IB, Nandakishore KJ, Sahu GK, Arul PT, James JM, Kareem SA. Root canal irrigants and irrigation techniques: A review. Journal of Evolution of Medical and Dental Sciences. 2015 Apr 2;4(27):4694-701.
14.Tekin B, Demirkaya K. Natural irrigation solutions in endodontics. Gu?lhane Tip Dergisi. 2020 Sep 1;62(3):133.
15. Mancini M, Armellin E, Casaglia A, Cerroni L, Cianconi L. A comparative study of smear layer removal and erosion in apical intraradicular dentine with three irrigating solutions: a scanning electron microscopy evaluation. Journal of endodontics. 2009 Jun 1;35(6):900-3.
16. Mittal A, Dadu S, Yendrembam B, Abraham A, Singh NS, Garg P. Comparison of new irrigating solutions on smear layer removal and calcium ions chelation from the root canal: An in vitro study. Endodontology 2018;30:55-61.
17. Singla MG, Relhan N, Aggarwal H. Comparative evaluation of oxytetracycline versus QMix, MTAD, and ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid as smear layer removal agents: An in vitro study. Endodontology 2018;30:2-8.
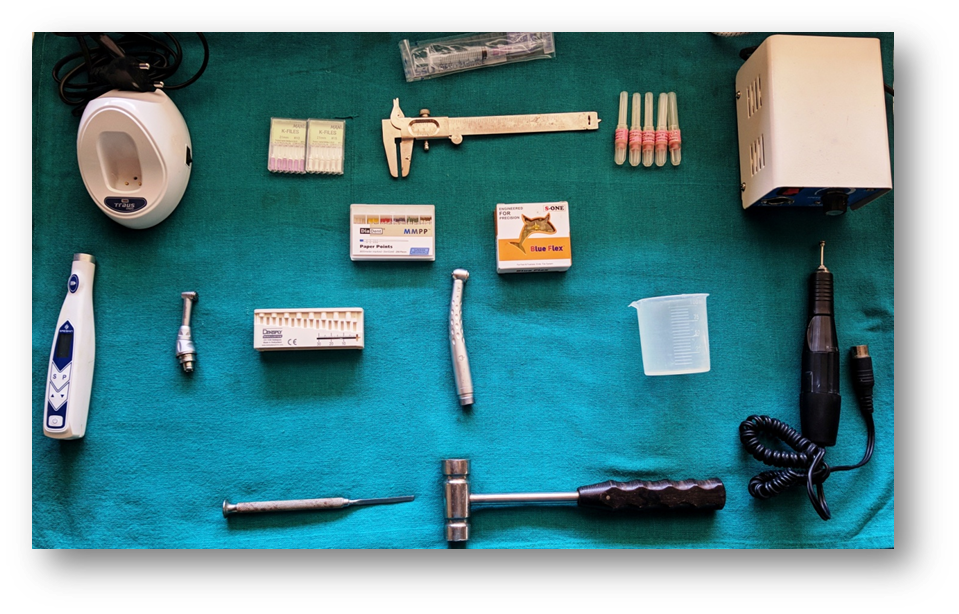
Figure 1
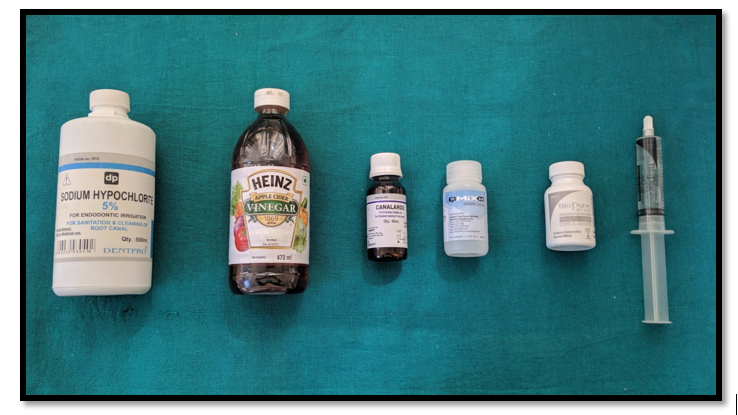
Figure 2
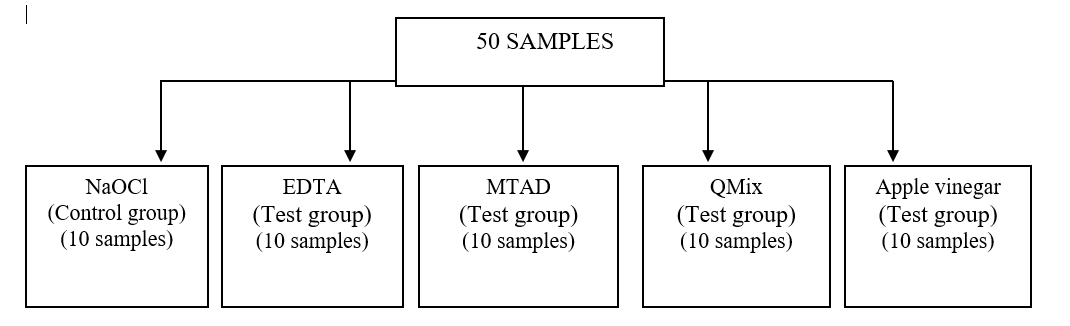
Figure 3
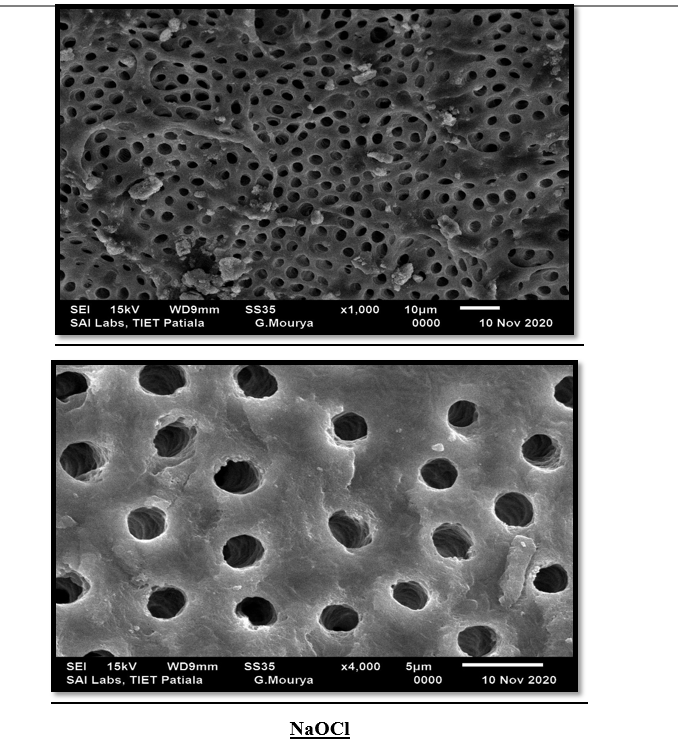
Figure 4
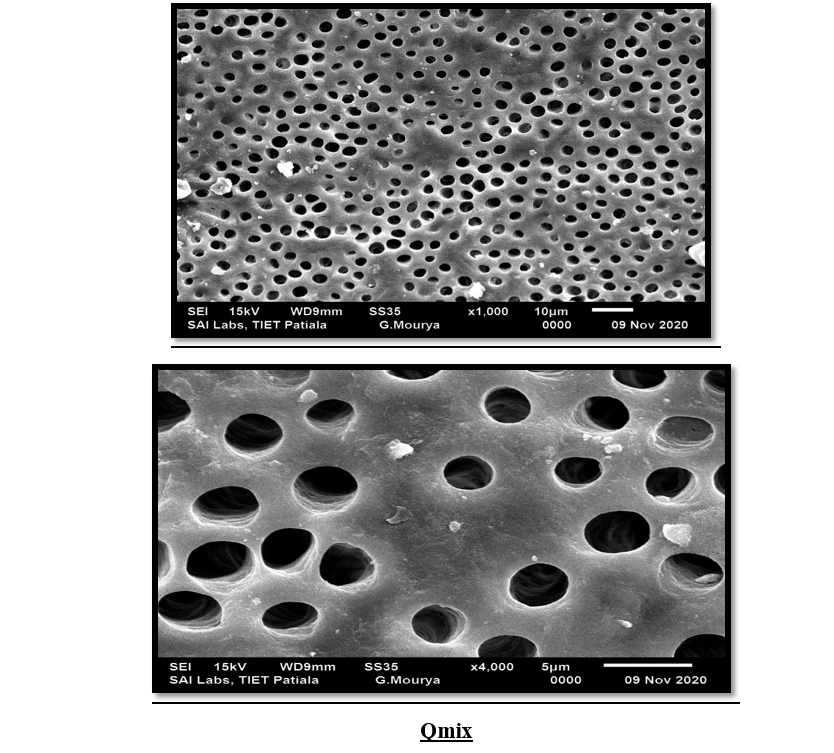
Figure 5
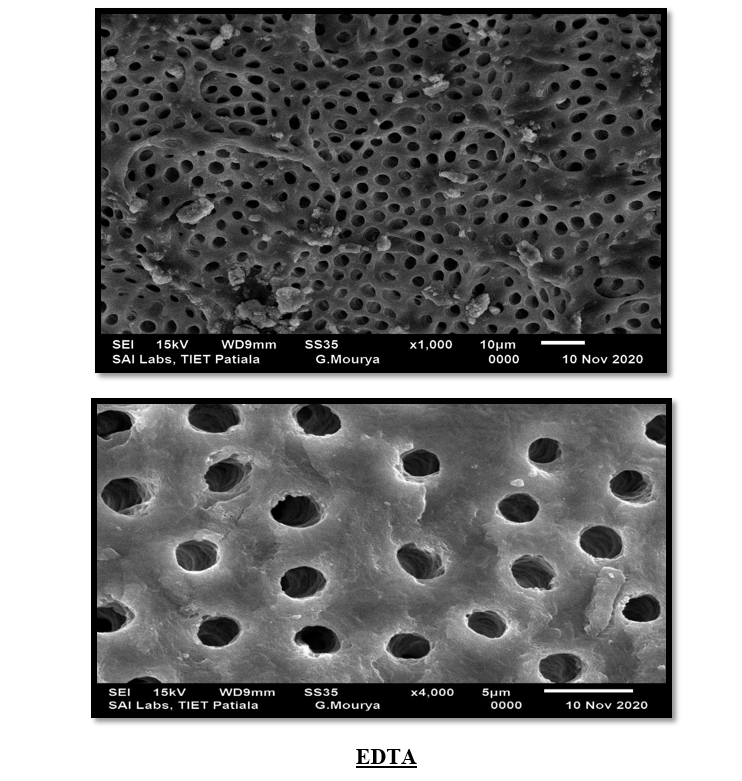
Figure 6
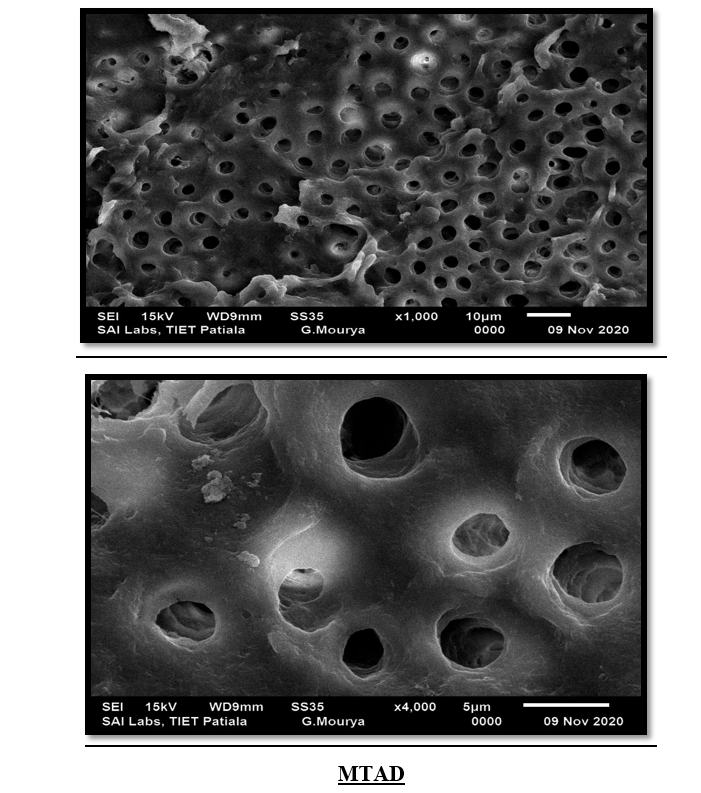
Figure 7
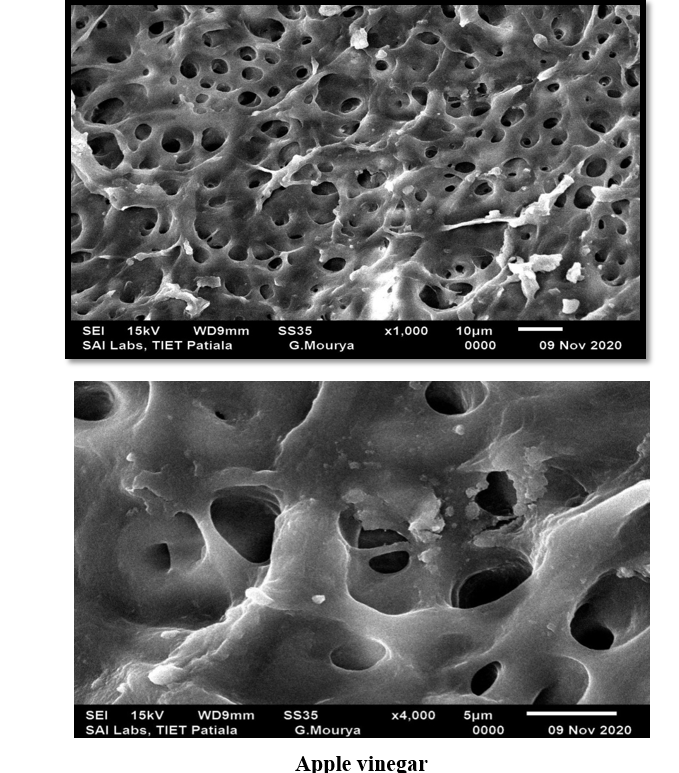
Figure 8
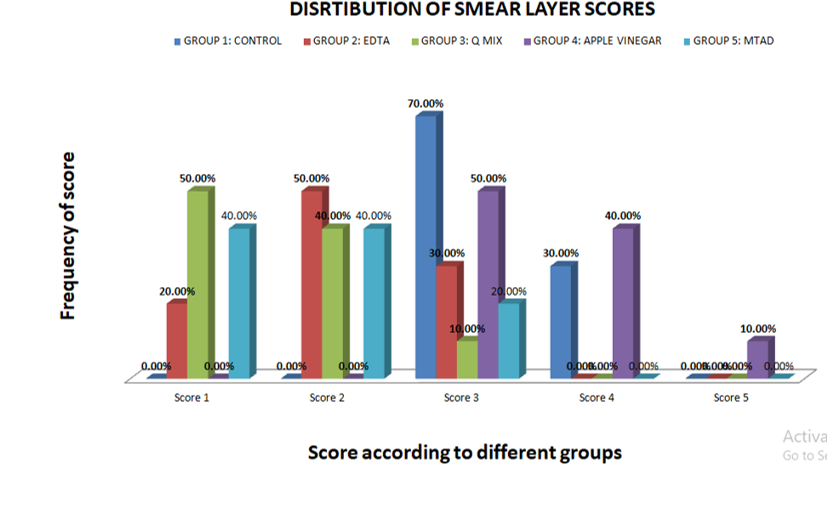
Figure 9
