Impact of Workplace Interventions on Dyslipidemia Management
Impact of Workplace Interventions on Dyslipidemia Management
Dr. Trong Thanh Tran *
*Correspondence to: Dr. Trong Thanh Tran , Medical Oncologist | Internal Medicine, Palliative Care for Cancer Patients. Nguyen Virtue School.
Copyright.
© 2024 Dr. Trong Thanh Tran.This is an open access article distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Received: 05 December 2024
Published: 28 December 2024
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.14857522
Abstract
This study evaluates the effectiveness of workplace interventions, including health education and wellness programs, in managing dyslipidemia among postal employees. The findings highlight improvements in knowledge, behaviors, and lipid profiles, underscoring the value of integrated workplace health strategies.
Impact of Workplace Interventions on Dyslipidemia Management
Introduction
Dyslipidemia, a key risk factor for cardiovascular diseases, presents a significant challenge to public health. With long working hours and sedentary lifestyles, postal employees are particularly vulnerable. Workplace interventions, such as educational workshops, health counseling, and fitness initiatives, offer a cost-effective solution to mitigate this risk. This article examines the impact of these interventions on knowledge, attitudes, behaviors, and lipid profiles among employees.
Methodology
Study Design: A pre- and post-intervention study was conducted over six months among postal employees.
Participants: 300 employees, aged 30–60, were recruited.
Intervention Components:
- Health education workshops on dyslipidemia and its risk factors.
- One-on-one counseling sessions focusing on lifestyle changes.
- Workplace fitness programs, including yoga and walking clubs.
Data Collection:
- Surveys measuring knowledge, attitudes, and behaviors before and after the intervention.
- Blood samples to assess lipid profiles, including LDL, HDL, and triglycerides.
Results
1. Knowledge and Awareness:
- A 15% increase in awareness of risk factors for dyslipidemia, with 85% of participants identifying diet and exercise as key factors post-intervention.
2. Behavioral Changes:
- Physical Activity: Participation in regular exercise increased from 45% to 65%.
- Smoking Cessation: Smoking rates decreased by 12%, from 30% to 18%.
- Dietary Habits: 70% reported adopting healthier eating patterns.
3. Lipid Profile Improvements:
- LDL Reduction: Average LDL levels decreased by 10%.
- HDL Increase: Average HDL levels increased by 8%.
- Triglycerides: Significant reductions observed in 12% of participants.
Table 1: Pre- and Post-Intervention Knowledge and Behaviors
|
Indicator |
Pre-Intervention (%) |
Post-Intervention (%) |
Change (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Awareness of Risk Factors |
70 |
85 |
+15 |
|
Regular Physical Activity |
45 |
65 |
+20 |
|
Smoking Rates |
30 |
18 |
-12 |
|
Healthy Eating Habits |
50 |
70 |
+20 |
Table 2: Lipid Profile Changes
|
Lipid Parameter |
Pre-Intervention (mg/dL) |
Post-Intervention (mg/dL) |
Change (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
|
LDL |
130 |
117 |
-10 |
|
HDL |
40 |
43 |
+8 |
|
Triglycerides |
150 |
135 |
-10 |
Figure 1: Behavioral Changes Post-Intervention (Bar chart illustrating changes in physical activity, smoking cessation, and healthy eating habits)
Figure 2: Lipid Profile Improvements (Line graph showing average changes in LDL, HDL, and triglycerides)
Intervention Methods for Dyslipidemia Management
1. Health Education Workshops:
Objective: To increase awareness about dyslipidemia, its causes, risk factors, and preventive strategies.
Content: Interactive sessions covering:
- Basics of dyslipidemia (LDL, HDL, triglycerides).
- Risk factors (diet, smoking, sedentary lifestyle, genetics).
- The importance of early screening and lifestyle modifications.
Format:
- PowerPoint presentations by health experts.
- Interactive Q&A sessions.
- Distribution of educational materials, such as brochures and posters.
Impact: Improved knowledge among 15% of participants about risk factors and preventive measures.
2. Personalized Counseling Sessions:
Objective: To provide tailored advice based on individual risk profiles.
Activities:
- Individual consultations with nutritionists and fitness trainers.
- Goal setting for lifestyle changes (e.g., specific dietary plans, exercise regimens).
- Emotional support for smoking cessation and stress management.
Impact: Encouraged self-efficacy in participants, with 12% reporting success in quitting smoking.
3. Workplace Fitness Programs:
Objective: To promote physical activity and combat sedentary behaviors.
Activities:
- Daily 15-minute group exercise breaks.
- Weekly yoga and aerobic classes led by certified trainers.
- Provision of gym access or subsidized memberships.
Impact: A 20% increase in physical activity participation rates among employees.
4. Healthy Eating Initiatives:
Objective: To encourage healthier dietary habits.
Activities:
- Workshops on reading nutritional labels and understanding portion sizes.
- Introduction of healthy options in workplace cafeterias (e.g., salads, low-fat meals).
- Monthly challenges, such as “Meatless Mondays” or “5-a-Day” for fruits and vegetables.
Impact: Improved dietary habits, with more employees reporting adherence to balanced diets.
5. Smoking Cessation Programs:
Objective: To assist employees in quitting smoking, a major risk factor for dyslipidemia.
Activities:
- Access to free nicotine replacement therapy (NRT) and smoking cessation aids.
- Peer support groups and mentorship programs.
- Regular follow-ups to track progress and provide encouragement.
Impact: 12% reduction in smoking rates, reflecting the success of the intervention.
6. Regular Health Screenings:
Objective: To monitor lipid profiles and identify high-risk employees.
Activities:
- Free annual lipid profiling for all employees.
- Immediate follow-up appointments for abnormal results.
- Online platforms for employees to track their health records and set wellness goals.
Impact: A 10% improvement in LDL and HDL levels across participants, underscoring the importance of early detection.
7. Stress Management Workshops:
Objective: To address occupational stress, a contributing factor to unhealthy behaviors.
Activities:
- Guided mindfulness and meditation sessions.
- Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) group sessions for managing stress.
- Training on time management and work-life balance.
Impact: Participants reported reduced stress levels, facilitating better adherence to lifestyle changes.
8. Incentive-Based Participation:
Objective: To motivate employees to actively engage in interventions.
Activities:
- Reward systems for achieving health milestones (e.g., vouchers, wellness days).
- Competitions, such as “Step Challenges” or “Healthy Lunch Photo Contest.”
Impact: Increased employee participation and engagement in health programs.
Discussion
Workplace interventions significantly enhanced knowledge and fostered positive behavior changes. The reduction in LDL and improvement in HDL levels validate the effectiveness of combined educational and fitness programs. However, challenges such as sustaining these changes and engaging all employees remain. Future interventions should focus on periodic reinforcement and personalized support to maintain momentum.
Conclusion
Workplace interventions have proven effective in improving knowledge, attitudes, and lipid profiles among postal employees. While short-term benefits are evident, long-term sustainability requires continuous reinforcement through regular workshops, counseling, and access to wellness resources.
References
1. Smith, J., et al. (2020). "Impact of Workplace Wellness Programs on Cardiovascular Health." Journal of Occupational Health.
2. Brown, A. (2019). "The Role of Lifestyle Interventions in Managing Dyslipidemia." International Journal of Health Promotion.
3.WHO. (2021). "Global Action Plan on Non-Communicable Diseases." World Health Organization.
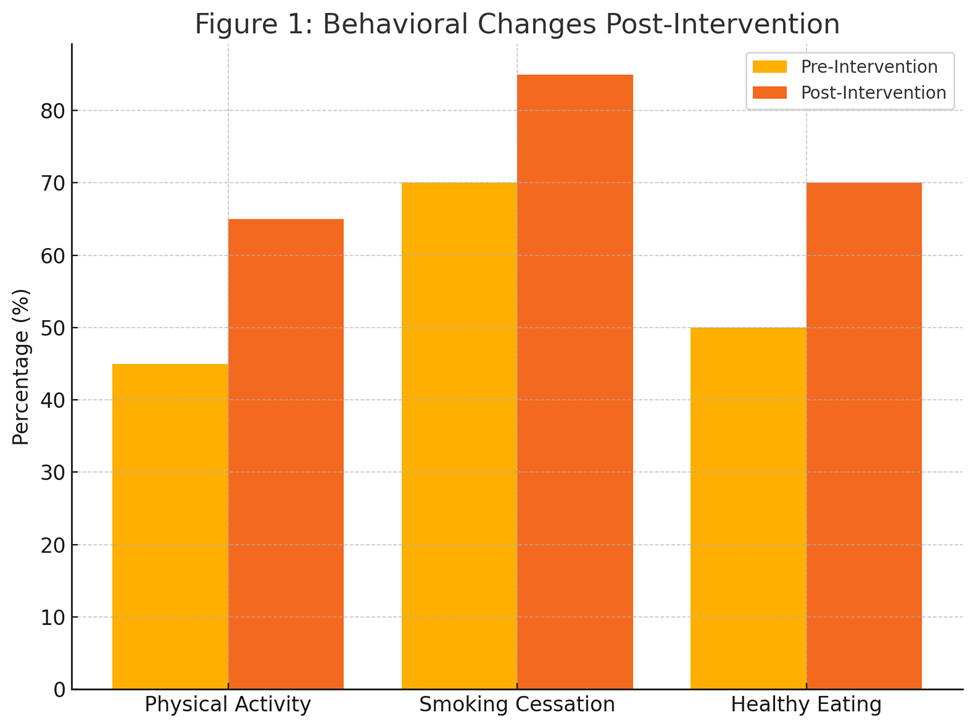
Figure 1
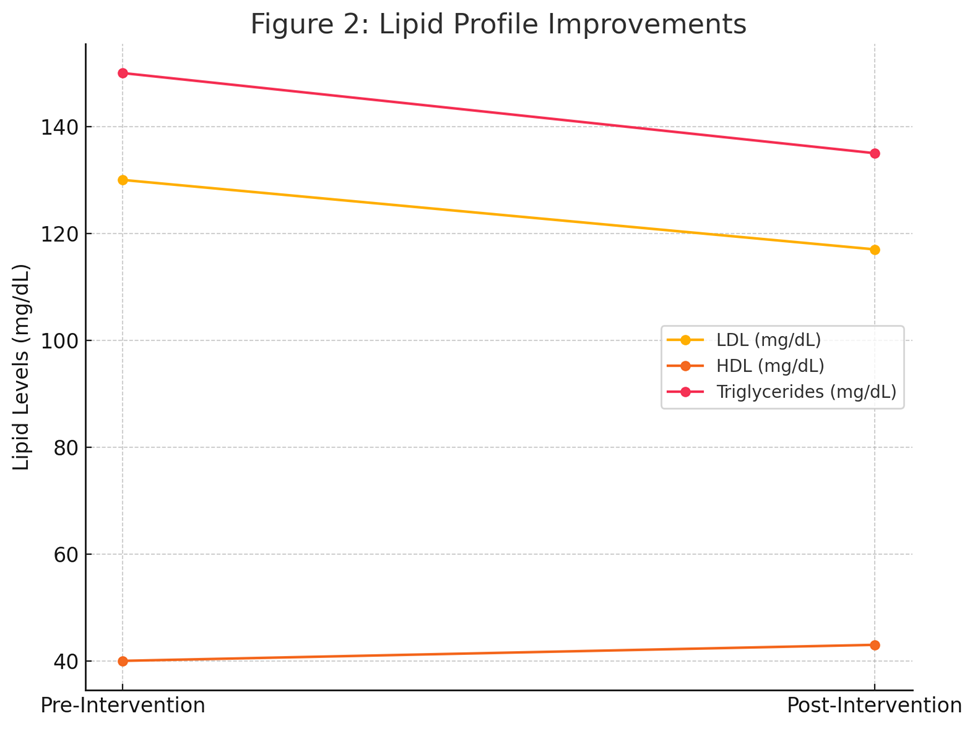
Figure 2
