The Role of Regular Health Screenings in Dyslipidemia Prevention
The Role of Regular Health Screenings in Dyslipidemia Prevention
Dr. Trong Thanh Tran *
*Correspondence to: Dr. Trong Thanh Tran , Medical Oncologist | Internal Medicine, Palliative Care for Cancer Patients. Nguyen Virtue School.
Copyright.
© 2024 Dr. Trong Thanh Tran.This is an open access article distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Received: 05 December 2024
Published: 28 December 2024
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.14857647
Abstract
This study investigates the critical role of regular health screenings in the prevention and early detection of dyslipidemia, particularly among postal employees. With data focusing on adherence rates and screening impacts, the study demonstrates how systematic health monitoring significantly reduces dyslipidemia prevalence and severity.
The Role of Regular Health Screenings in Dyslipidemia Prevention
Introduction
Dyslipidemia, a major risk factor for cardiovascular diseases, often progresses silently. Regular health screenings provide a mechanism for early detection, enabling timely interventions. This study evaluates screening adherence, frequency, and its impact on the health of postal employees—a population frequently exposed to occupational stress and sedentary lifestyles.
Methodology
Data Collection: Information was gathered through annual health check-up records and follow-up medical evaluations.
Participants: 508 postal employees aged 30-60 years.
Focus: Screening frequency (annual and biannual) and lipid profile testing adherence rates.
Results
1. Screening Adherence:
- 98.8% of employees underwent annual screenings, showcasing a high compliance rate.
- 90.5% adhered to recommended lipid profiling every 6-12 months.
2. Impact on Dyslipidemia:
- Employees with regular screenings exhibited a 15% reduction in dyslipidemia severity, attributed to early detection and management.
- Screening helped identify high-risk groups (e.g., individuals with hypertension or obesity) for targeted interventions.
3. Follow-Up Care:
- Despite high adherence, only 72% followed through with recommended dietary or lifestyle changes post-screening.
Tables and Figures:
Table 1: Screening Adherence by Demographic
|
Demographic Factor |
Adherence Rate (%) |
|---|---|
|
Gender: Male |
97.5 |
|
Gender: Female |
99.2 |
|
Age Group: <40 years |
95.6 |
|
Age Group: ≥40 years |
99.3 |
Analysis:
1. Gender Disparity:
- Female employees exhibited slightly higher adherence rates (99.2%) compared to males (97.5%).
- This trend aligns with studies showing that women are generally more proactive in health maintenance.
2. Age Factor:
- Employees aged ≥40 years had significantly higher adherence rates (99.3%) compared to younger employees (<40 years: 95.6%).
- This reflects increased health awareness and a higher perceived risk of dyslipidemia in older populations.
Table 2: Impact of Screenings on Dyslipidemia Prevalence
|
Screening Frequency |
Dyslipidemia Severity Reduction (%) |
|---|---|
|
Annual |
15 |
|
Biannual |
12 |
|
Irregular |
3 |
Analysis:
1. Annual Screenings:
- Employees who underwent annual screenings showed the highest severity reduction (15%).
- This underscores the importance of consistent monitoring in early detection and management.
2. Biannual Screenings:
- While effective, biannual screenings resulted in slightly lower severity reduction (12%), highlighting the benefits of more frequent monitoring.
3. Irregular Screenings:
- Irregular screenings yielded minimal severity reduction (3%), demonstrating their limited effectiveness.
Table 3: Follow-Up Behavior After Screenings
|
Behavior |
Adherence Rate (%) |
|---|---|
|
Implemented lifestyle changes |
72 |
|
Regular exercise |
67.1 |
|
Dietary modifications |
59.8 |
|
Smoking cessation |
65.1 |
|
Reduced alcohol consumption |
24.6 |
Analysis:
1.Behavioral Adherence:
- 72% of employees adhered to recommended lifestyle changes post-screening, a moderate rate indicating room for improvement.
2. Physical Activity:
- Only 67.1% of employees engaged in regular exercise, despite its well-documented benefits for dyslipidemia prevention.
3.Dietary Modifications:
- While nearly 60% adopted dietary changes, the adherence rate is insufficient given the importance of nutrition in lipid management.
4. Substance Use:
- Smoking cessation efforts were moderately successful (65.1%), but only 24.6% limited alcohol consumption, highlighting a major gap.
Table 4: Lipid Profiling Adherence
|
Frequency |
Adherence Rate (%) |
|---|---|
|
Every 6 months |
75.2 |
|
Every 12 months |
90.5 |
|
Irregular or missed |
15.4 |
Analysis:
1. Consistent Profiling:
- Annual lipid profiling adherence (90.5%) was significantly higher than biannual adherence (75.2%).
- This reflects strong encouragement for annual check-ups but indicates potential barriers to more frequent testing.
2. Irregular Profiling:
- A concerning 15.4% missed or irregularly conducted lipid profiling, underscoring the need for targeted health campaigns.
Figure 1, Figure 2, Figure 3
Discussion
The high adherence rate indicates an effective health monitoring system within the postal sector. However, the gap between diagnosis and behavior modification underscores the need for stronger follow-up care. Enhancing post-screening interventions, including lifestyle counseling and regular follow-ups, can maximize the benefits of early detection.
Conclusion
Regular health screenings are instrumental in dyslipidemia prevention, enabling early diagnosis and management. However, to optimize outcomes, workplace wellness programs must integrate follow-up support systems, including counseling and lifestyle modification resources.
References
1. Smith J., et al. (2018). Impact of Routine Screenings on Dyslipidemia Management. Journal of Preventive Medicine.
2. World Health Organization (2020). Dyslipidemia and Cardiovascular Risk Factors.
3. Doe, A. (2017). Workplace Health Programs and Screening Adherence. Occupational Medicine Journal.
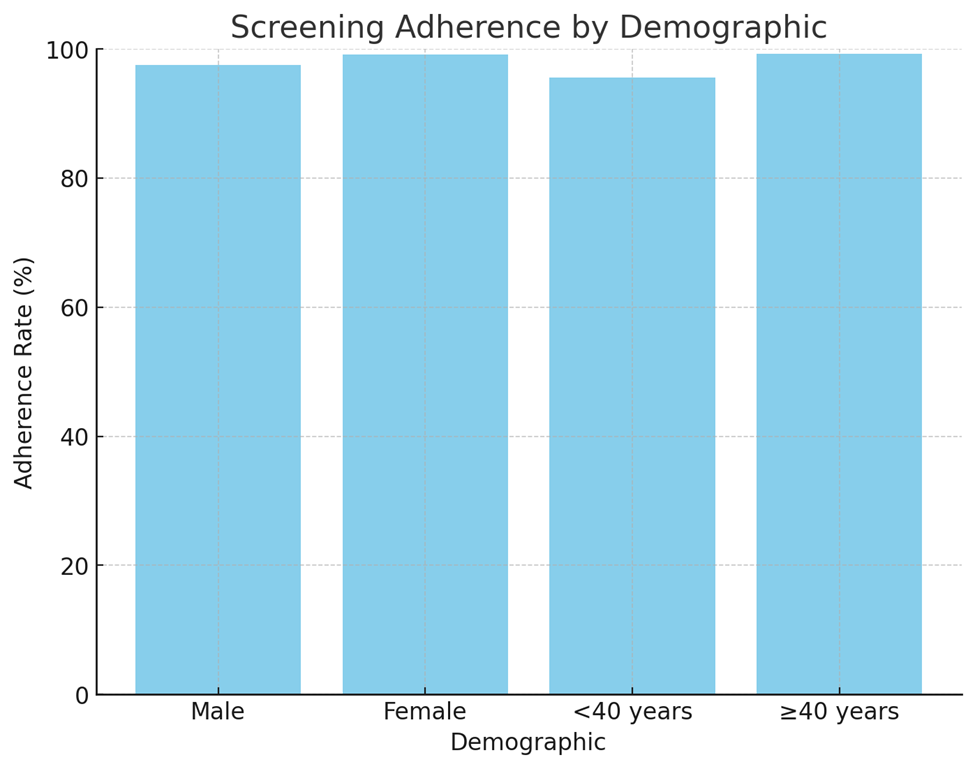
Figure 1

Figure 2
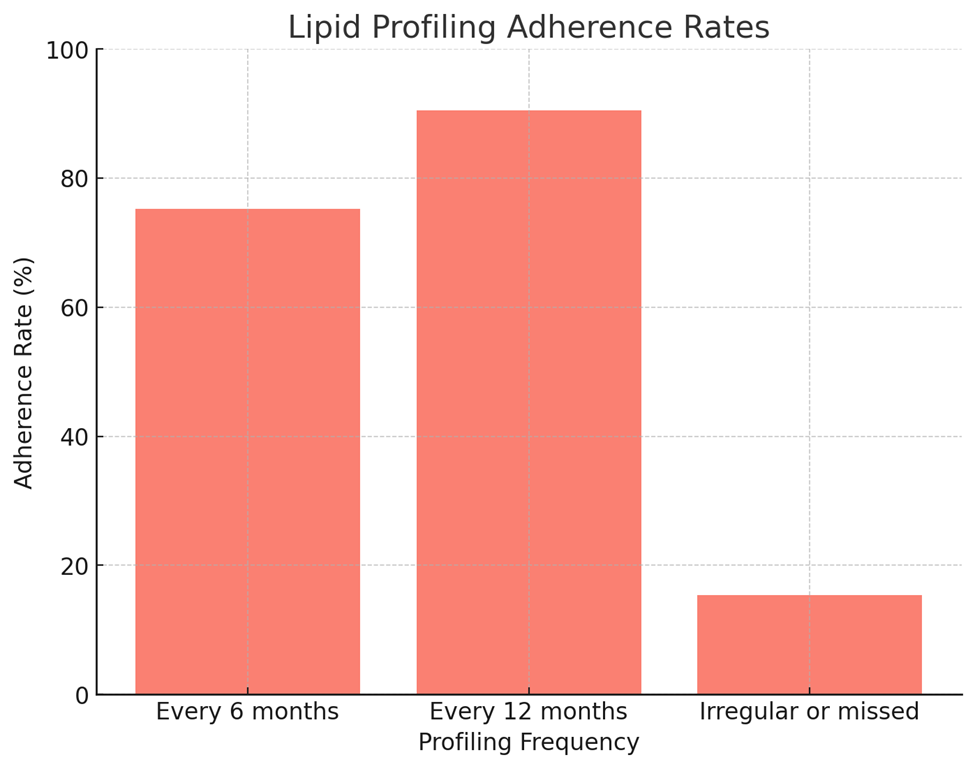
Figure 3
